The Essence of Kerala Style Homes
Kerala style architecture, a testament to the rich cultural heritage of the region, is characterized by its simplicity, functionality, and harmonious integration with the natural environment. It’s a style that has evolved over centuries, shaped by the unique climate, landscape, and cultural traditions of Kerala.
Defining Characteristics, 4 bedroom house plans kerala style
Kerala style homes are known for their distinctive features that reflect the region’s climate and lifestyle. These features include:
- Sloping Roofs: The signature feature of Kerala homes is their sloping roofs, typically made of “nalukettu” – a traditional tile made from baked clay. These roofs are designed to effectively shed heavy monsoon rains and provide ample ventilation. They are often adorned with intricate wooden carvings and decorative elements, adding to the aesthetic appeal of the homes.
- Verandahs: Spacious verandahs, often extending around the entire house, are integral to Kerala homes. These verandahs serve as a transition space between the interior and exterior, providing shade from the sun and a comfortable area for relaxation and social gatherings.
- Courtyard Spaces: Kerala homes often incorporate courtyards, which serve as a central gathering space and provide natural light and ventilation to the house. They are typically planted with trees and flowering plants, creating a serene and inviting atmosphere.
- Use of Natural Materials: Kerala architecture emphasizes the use of natural materials such as wood, bamboo, and laterite. These materials are readily available in the region and contribute to the sustainable and eco-friendly nature of Kerala homes.
- Open Plan Layout: Kerala homes often feature an open plan layout, with minimal walls and partitions. This creates a sense of spaciousness and allows for natural light and air to circulate freely throughout the house.
Cultural and Historical Influences
The development of Kerala style architecture is deeply rooted in the region’s culture and history. The influence of ancient Indian architectural traditions, particularly the Dravidian style, is evident in the use of sloping roofs, intricate carvings, and the emphasis on symmetry and balance.
The region’s tropical climate has also played a significant role in shaping Kerala architecture. The use of natural materials, open plan layouts, and sloping roofs are all adaptations to the hot and humid climate.
Traditional Kerala House Features
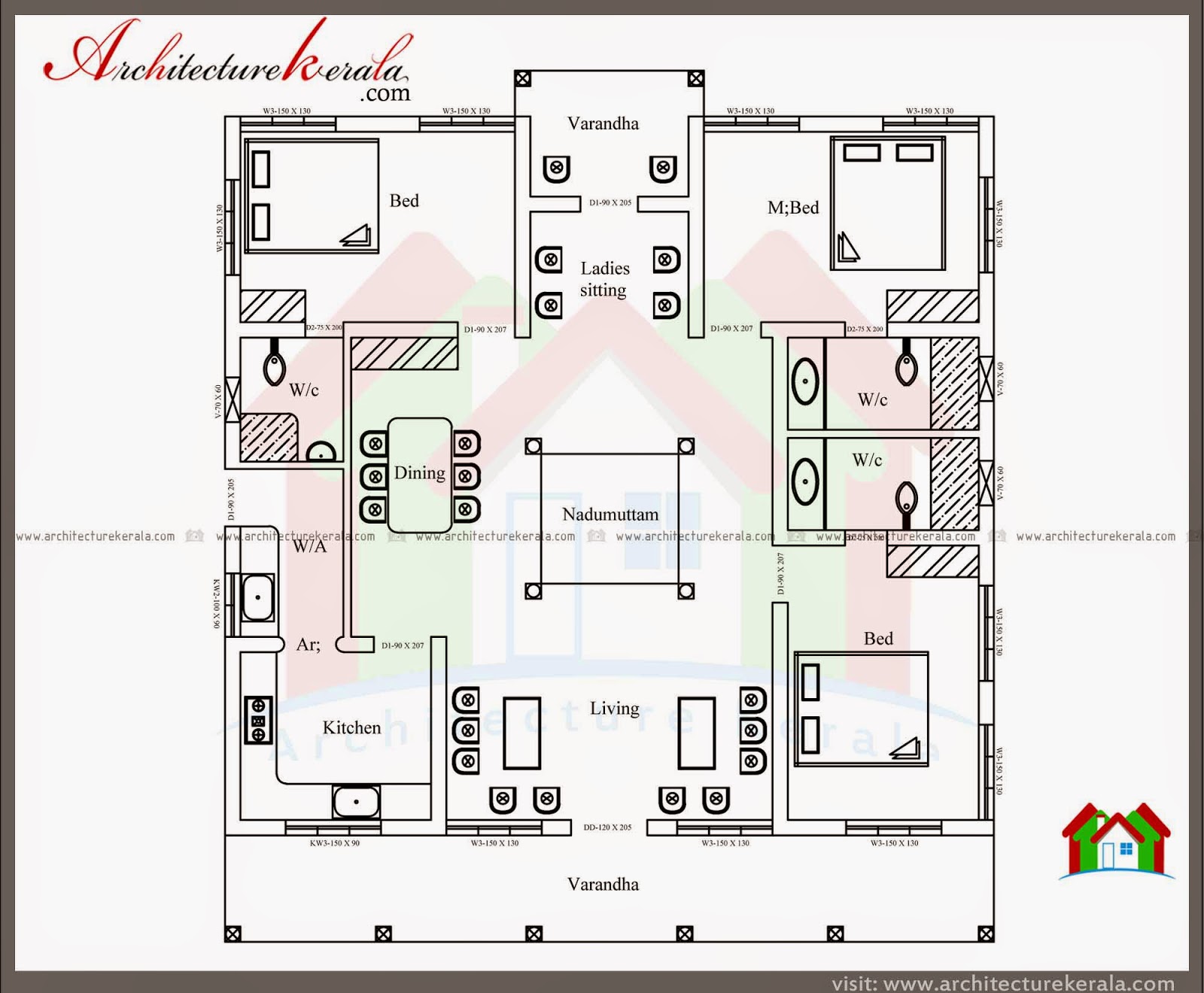
- Nalukettu: The traditional Kerala house, known as a “nalukettu,” is a rectangular structure with four wings, each representing a different aspect of life. The central courtyard is the heart of the house, symbolizing unity and harmony. This traditional design has evolved over centuries, with variations in size and layout depending on the social status and needs of the family.
- Tharavadu: A larger and more elaborate version of the nalukettu, the “tharavadu” is a traditional joint family house that houses multiple generations. It is characterized by its spacious courtyard, multiple rooms, and elaborate wooden carvings. The tharavadu represents the importance of family and community in Kerala culture.
- Traditional Carvings: Wooden carvings are an integral part of Kerala architecture, adorning the doors, windows, and ceilings of homes. These carvings are often intricate and depict scenes from mythology, folklore, and everyday life. They add a touch of artistry and elegance to Kerala homes.
- Laterite Walls: Laterite, a reddish-brown sedimentary rock, is widely used in Kerala architecture for building walls. This material is readily available in the region and has excellent thermal properties, keeping homes cool in the summer and warm in the winter.
Materials and Construction Techniques: 4 Bedroom House Plans Kerala Style

Kerala style homes are renowned for their sustainable and eco-friendly construction practices, often incorporating traditional building materials that blend seamlessly with the natural surroundings. The use of these materials not only contributes to the aesthetic appeal of the homes but also promotes a sense of connection with the environment.
Traditional Building Materials
Traditional Kerala homes are characterized by the use of natural materials like wood, bamboo, and laterite.
- Wood: Timber, primarily from teak, rosewood, and jackfruit trees, has been a staple in Kerala construction. It is used for beams, columns, doors, windows, and decorative elements, offering durability and a rich aesthetic.
- Bamboo: Bamboo, readily available in the region, serves as a versatile material for roofing, walls, and even furniture. Its lightweight, flexible nature, and rapid growth rate make it a sustainable and cost-effective choice.
- Laterite: This reddish-brown soil found in Kerala is a natural building stone used for walls and foundations. Its porous nature allows for thermal insulation, keeping the house cool in hot weather.
Modern Interpretations of Traditional Materials
While traditional materials remain integral to Kerala architecture, modern interpretations have evolved to address contemporary needs and sustainability concerns.
- Engineered Timber: Modern techniques utilize engineered timber, like laminated veneer lumber (LVL) and glulam beams, which offer greater strength and dimensional stability compared to traditional timber. This allows for larger spans and more complex designs.
- Sustainable Bamboo: Bamboo is increasingly used in modern construction, with advancements in processing and treatment techniques enhancing its durability and fire resistance. Bamboo flooring, walls, and even structural elements are becoming popular choices.
- Recycled and Upcycled Materials: The use of recycled and upcycled materials, such as reclaimed wood and repurposed bricks, is gaining traction. This practice aligns with sustainable construction principles and adds a unique character to the homes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional vs. Modern Materials
- Traditional Materials:
- Advantages:
- Natural and sustainable
- Good thermal insulation
- Aesthetics and traditional charm
- Disadvantages:
- Susceptibility to termites and weather damage
- Limited availability of certain wood species
- Higher maintenance requirements
- Advantages:
- Modern Materials:
- Advantages:
- Increased strength and durability
- Lower maintenance requirements
- Greater design flexibility
- Disadvantages:
- Higher initial cost
- May not be as aesthetically pleasing as traditional materials
- Environmental impact of manufacturing processes
- Advantages:
